The lube kitchen part 7: detergent additives – keeping your parts clean
This article has been supplied.
By: Steven Lumley - technical manager, WearCheck
(Virtual Showroom) The topic of oil additives is vast, and Steven Lumley - technical manager for WearCheck - continues the conversation around these essential components of a good engine-management programme, this time with a new focus: detergent additives.
Detergents play an important behind-the-scenes role in our everyday lives – they remove stains from our clothes, clean our floors, wash our hair and yes, they even keep our engines clean. Detergents are essentially cleansing agents which combine with impurities to make them more soluble in a given medium. And for those budding etymologists out there, the word detergent is derived from the Latin verb detergere, which means to wipe off, or cleanse.
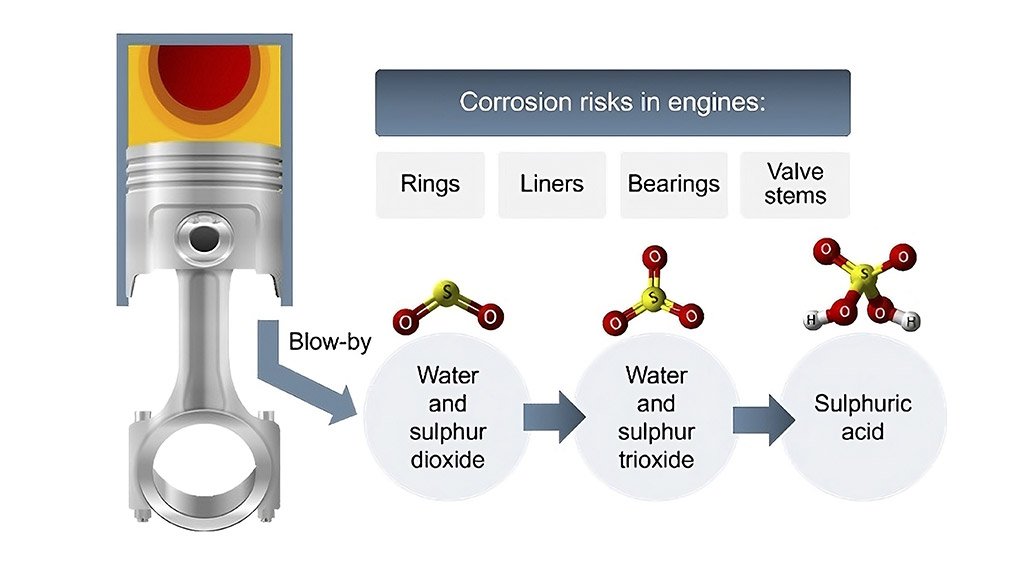
Detergents in lubricants are cleaning agents that contain metals. They are primarily used in engine oils and are mostly alkaline or basic in nature. They work in the high-temperature combat zone of the engine (rings, pistons, liners and vales) to keep surfaces free of deposits, especially at ring grooves. They also neutralise harmful acids generated by the combustion of fuel, and provide rust protection.
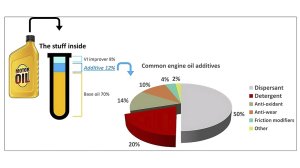
The first engine-oil detergents, (calcium carboxylate and phosphonate) were developed in the early 1940s and - by the 1950s - the engine-oil market had exploded, with lubricants containing over-based sulphonates and salicylates. Interestingly enough, Calcium sulphonates still make up about 60% of total detergent consumption when it comes to finished engine lubricants.
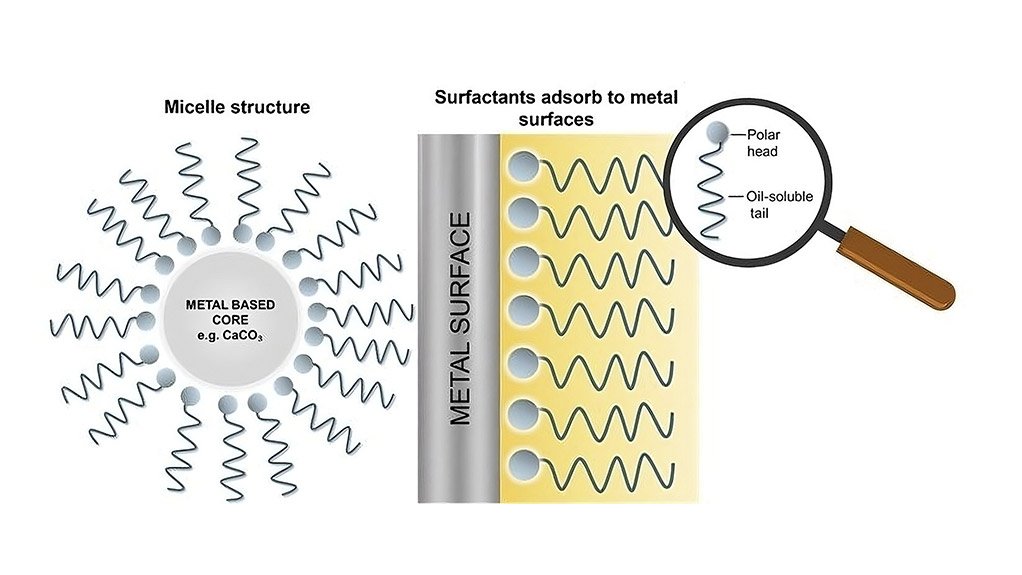
These cleaning agents are oil-soluble, organo-metallic compounds with polar heads, which allows them to cling to metal surfaces. Deposits and metal surfaces are both polar, and deposits are drawn to the metal surfaces and stick to them. The detergent additive, with its stronger charge, displaces these deposits from the metal surface.
Detergents have a similar structure to that of dispersant additives, with a polar head and a long, non-polar hydrophobic tail, but detergents contain a metal salt on an acidic organic molecule in their polar head.
Detergents and dispersants are the power couple of the engine-oil-additive world, and, as such, their relationship is synergistic in nature - while detergents remove deposits, they also work together with dispersants to keep these deposits in suspension in the oil by preventing the formation of large polar aggregates from settling on metal surfaces.
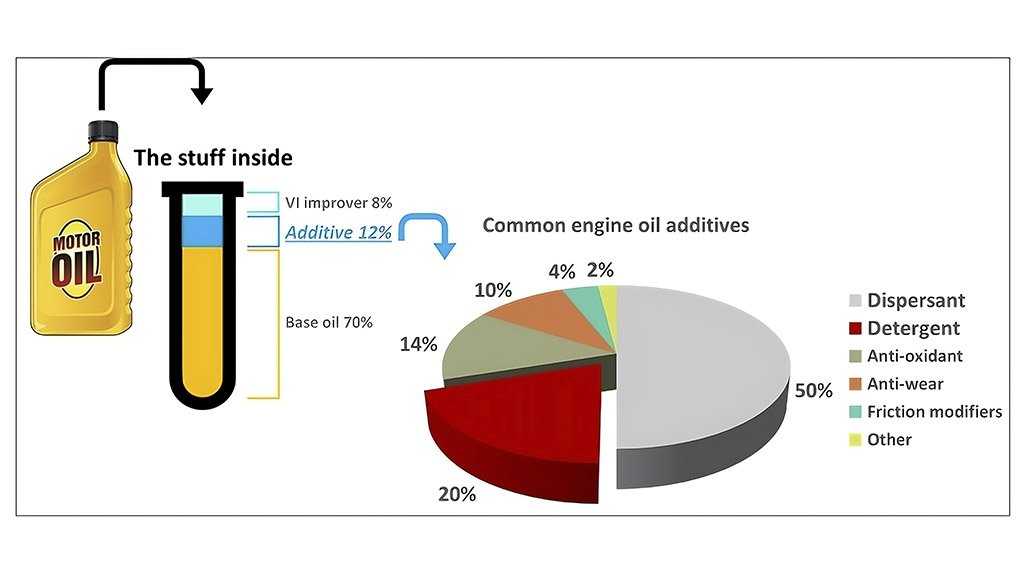
The additive treat rate of an engine oil is dependent on several factors, like the performance specification (e.g. API - American Petroleum Institute, JACO - Japanese Automotive Standards Organisation etc), the engine manufacturer’s approval, the type and viscosity of base oil, as well as the additive supplier, but - generally speaking - a fully formulated mineral engine oil would contain about 80% base oil, 8% VI (Viscosity Index) improver and around about 12% additive package. Of that 12%, detergent and dispersant additives make up between 55-70% so, it stands to reason that the chemistry of the total package and finished oil is greatly influenced by these two components and their interactions with each other.
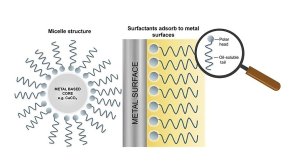
Now for the nifty chemistry part - detergents are composed of two components, a surfactant and a colloidal inorganic phase. The combination of a surfactant molecule with a colloidal inorganic core results in a micellar-type structure.
This basic colloidal carbonate neutralises acids formed during the combustion process, such as nitric and sulfuric acid, which can lead to metal corrosion and wear, as well as organic acids, which can lead to polymerisation and oil thickening. The all-important Total Base Number (TBN) of the oil is an expression of this neutralisation ability.
The surfactant component of the detergent forms a protective layer on metal surfaces, resulting in the prevention of deposit build-up, rust and corrosion. The surfactant and the basic components work together to inhibit rust and corrosion, oil degradation, reduce high-temperature deposits and solubilise polar components.
One of the main driving forces behind new engine-oil formulations is compatibility with exhaust aftertreatments systems, like DPFs (diesel particulate filters).
To protect these systems, new-generation engine oils must contain lower SAPS (Sulphated Ash, Phosphorus and Sulphur) levels since SAPS can poison, deactivate or block these emission-control, after-treatment devices. Due to their metallic nature, detergents in conventional engine oils are prone to producing residues and ash when burned in the engine, which, unfortunately, contributes to the SAPS level of the oil and can cause DPFs to block.
The move towards low-SAPS engine oils will result in a shift from traditional engine-oil technologies to alternative chemistries, with more focus on ashless, metal-free detergent additive systems.
Article Enquiry
Email Article
Save Article
Feedback
To advertise email advertising@creamermedia.co.za or click here
Press Office
Announcements
What's On
Subscribe to improve your user experience...
Option 1 (equivalent of R125 a month):
Receive a weekly copy of Creamer Media's Engineering News & Mining Weekly magazine
(print copy for those in South Africa and e-magazine for those outside of South Africa)
Receive daily email newsletters
Access to full search results
Access archive of magazine back copies
Access to Projects in Progress
Access to ONE Research Report of your choice in PDF format
Option 2 (equivalent of R375 a month):
All benefits from Option 1
PLUS
Access to Creamer Media's Research Channel Africa for ALL Research Reports, in PDF format, on various industrial and mining sectors
including Electricity; Water; Energy Transition; Hydrogen; Roads, Rail and Ports; Coal; Gold; Platinum; Battery Metals; etc.
Already a subscriber?
Forgotten your password?
Receive weekly copy of Creamer Media's Engineering News & Mining Weekly magazine (print copy for those in South Africa and e-magazine for those outside of South Africa)
➕
Recieve daily email newsletters
➕
Access to full search results
➕
Access archive of magazine back copies
➕
Access to Projects in Progress
➕
Access to ONE Research Report of your choice in PDF format
RESEARCH CHANNEL AFRICA
R4500 (equivalent of R375 a month)
SUBSCRIBEAll benefits from Option 1
➕
Access to Creamer Media's Research Channel Africa for ALL Research Reports on various industrial and mining sectors, in PDF format, including on:
Electricity
➕
Water
➕
Energy Transition
➕
Hydrogen
➕
Roads, Rail and Ports
➕
Coal
➕
Gold
➕
Platinum
➕
Battery Metals
➕
etc.
Receive all benefits from Option 1 or Option 2 delivered to numerous people at your company
➕
Multiple User names and Passwords for simultaneous log-ins
➕
Intranet integration access to all in your organisation